Key Takeaways
- Use disk space analyzer apps like Disk Space Analyzer on macOS and TreeSize on Windows to quickly locate large files.
- If you prefer not to use third-party apps, you can use the built-in storage tools available in Windows and macOS.
- While searching for large files, check for duplicates, storage consumed by virtual machines, backup files, and other space hogs.
Finding large files can be difficult, especially when they’re scattered across multiple drives and folders. However, with the right tools, figuring out what files are taking up the most space becomes a simple task.
1 Use Third-Party Disk Space Analyzers
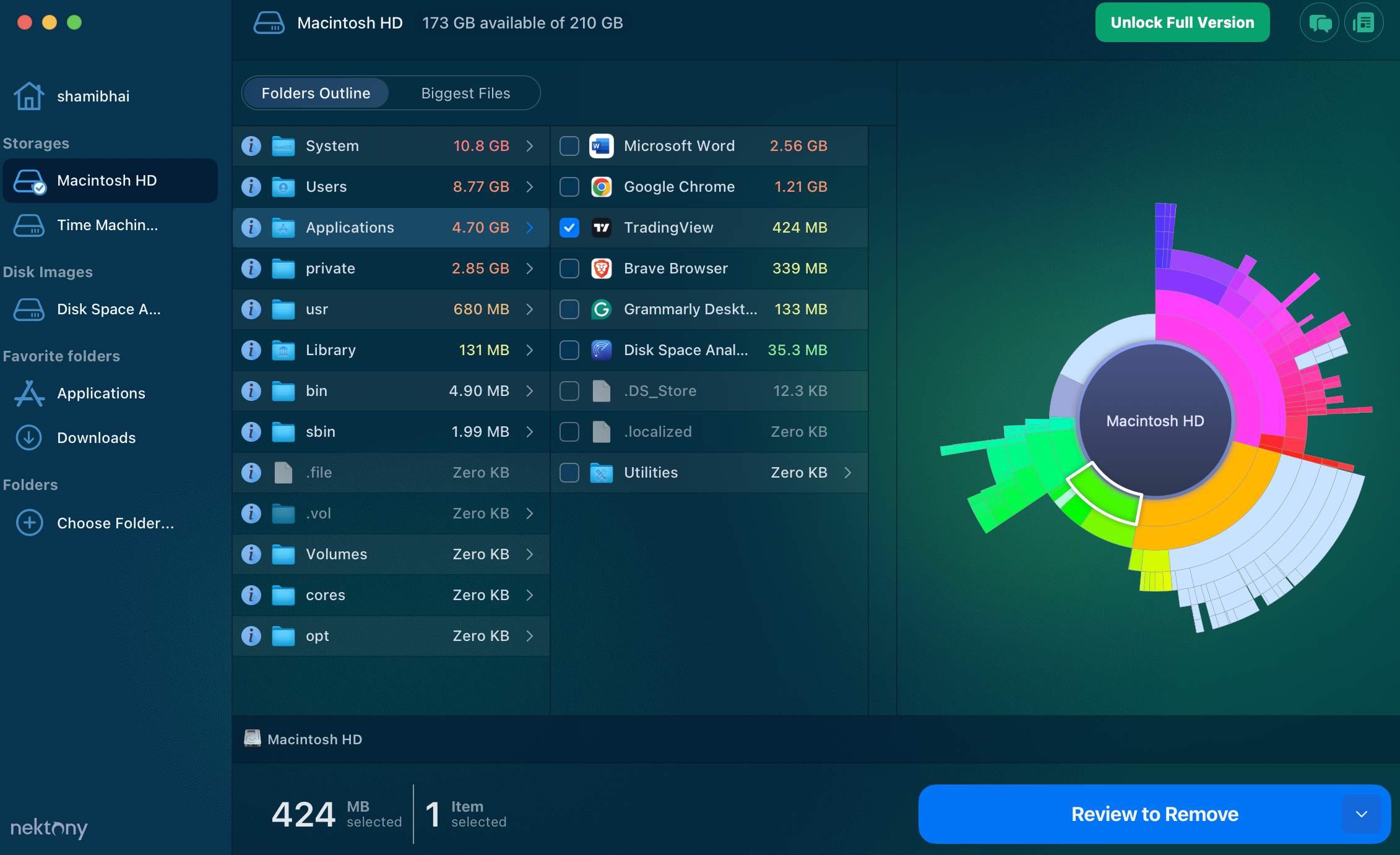
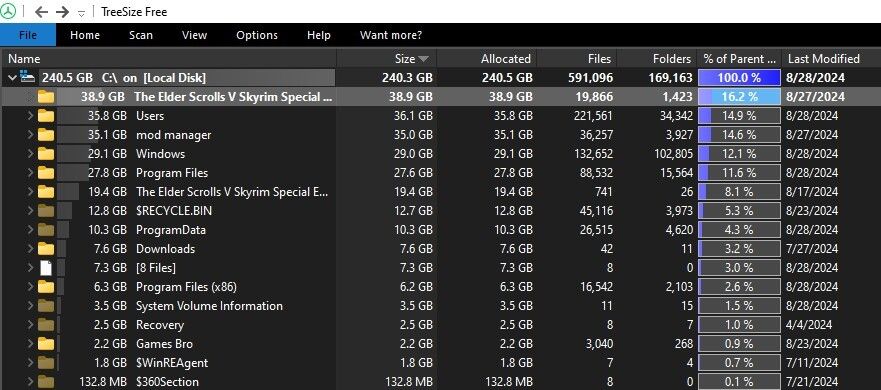
Disk space analyzer apps scan your storage drive and list files by size in descending order, putting the largest files at the top. This makes it easy to identify which data is consuming the most space. I use the Disk Space Analyzer app for this task on macOS, while on Windows, I use TreeSize.
How to Use Disk Space Analyzer on macOS
- Download and install the Disk Space Analyzer app from the App Store.
- Launch the app, select the storage drive you want to scan from the left sidebar, and click Start Scanning.
- Grant any necessary permissions and allow the app to complete the scan.
- Select the data you want to remove, click Review to Remove, and then select Remove.
Repeat these steps for all large files.
How to Use TreeSize on Windows
- Download and install TreeSize app.
- Launch the app as an administrator, go to the Scan tab, click Select Directory, and choose the drive you want to scan.
- Wait a moment; the app will display large files sorted in descending order by size.
- Expand folders that take up the most space and delete unnecessary files to free up storage space.
- You can click on the top of the Last Modified column to see large files that haven’t been used recently.
Work through the list and remove any large files you no longer need.
If you prefer not to use third-party apps, Windows and macOS offer built-in tools to help you scan for and delete large files.
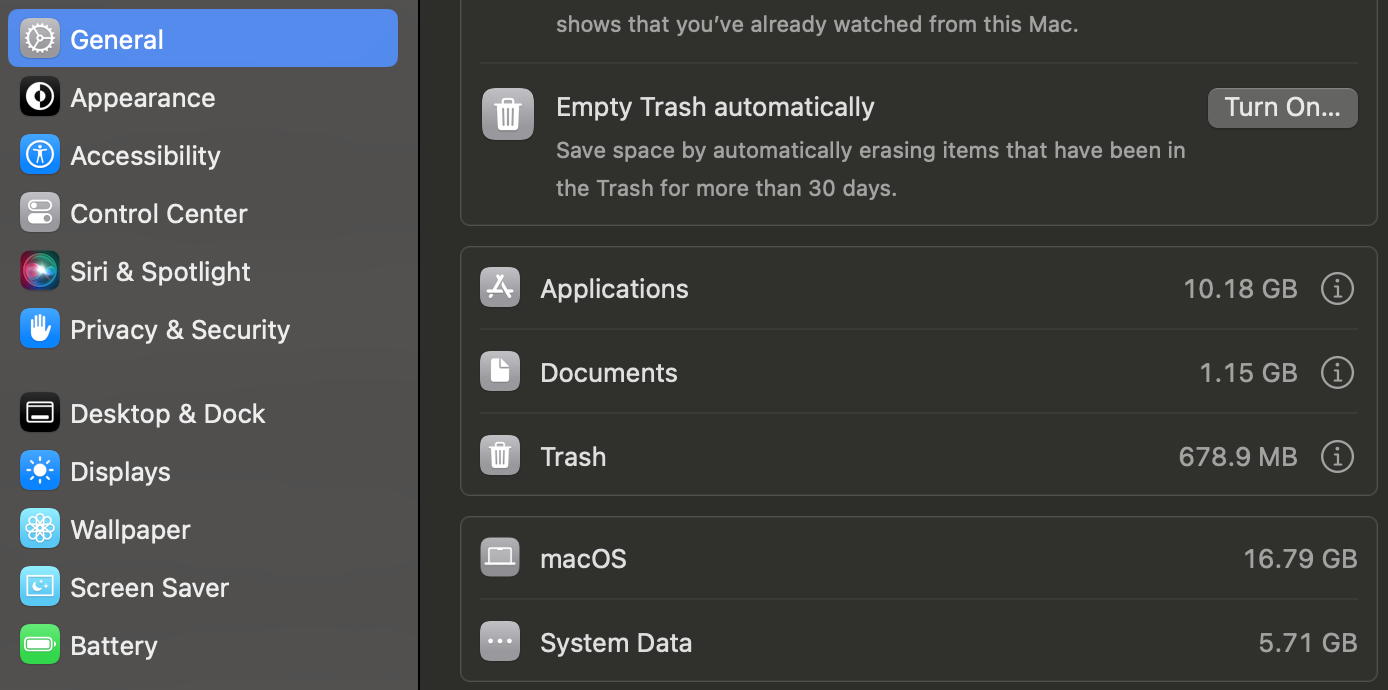
macOS
- Click the Apple menu in the top-left corner and select System Settings.
- Navigate to General > Storage, where macOS will display the applications, documents, and system data consuming storage space.
- Click the information symbol (ⓘ) next to the type of data using the most space, select the file or app you want to remove, and click Delete.
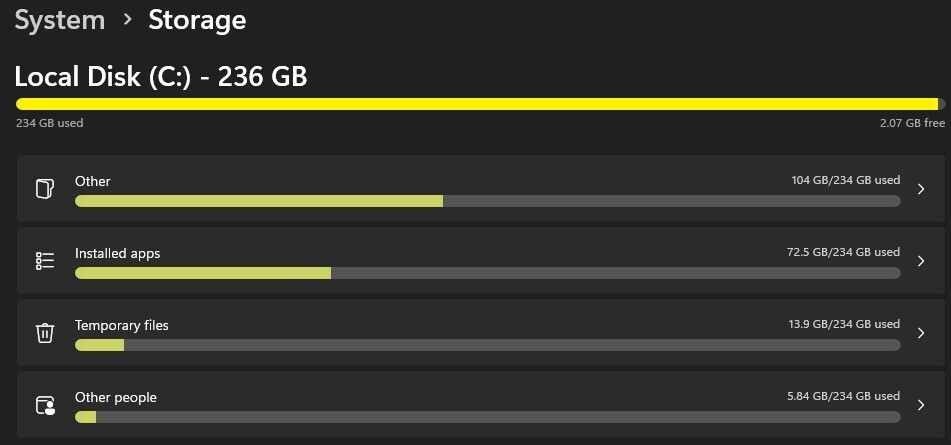
Windows
- Right-click the Start button and open Settings.
- Go to System > Storage and wait for Windows to scan for data using the most storage. Open folders like “Other” or “Installed Apps” to see which items take up the most space, listed in descending order by size.
- Delete any unnecessary data to free up storage space.
You can also manually search for large files in specific folders. Select the drive or folder you want to scan on Windows, type “size: gigantic” in the search bar, and arrange the results by file size to find the largest files. On macOS, select the directory you want to scan, and type “size:>size in bytes” into the search bar. macOS will filter files larger than that size.
3 Don’t Forget These Unusual Space Hogs
When checking for folders and applications that consume the most real estate on your storage drive, keep an eye out for duplicate files, as they unnecessarily take up valuable storage space. For detailed instructions, refer to our guide on finding and removing duplicate data from your Windows PC or macOS device.
If you’ve used virtual machines in the past, it’s worth checking if they’re taking up significant storage on your drive. If your virtualization software offers a “dynamically allocated storage” option for virtual disks, consider enabling it. This feature allows VMs to occupy only the storage they actually need rather than the total amount allocated to them.
Backups can also take up a lot of space because they often duplicate large amounts of data, store multiple versions of files, and include redundant data for safety. If you regularly perform full backups instead of incremental ones, this can add to the storage burden. So, switch to incremental backups and reduce the frequency of your backups to alleviate this issue.